Navigating Foraminal Stenosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
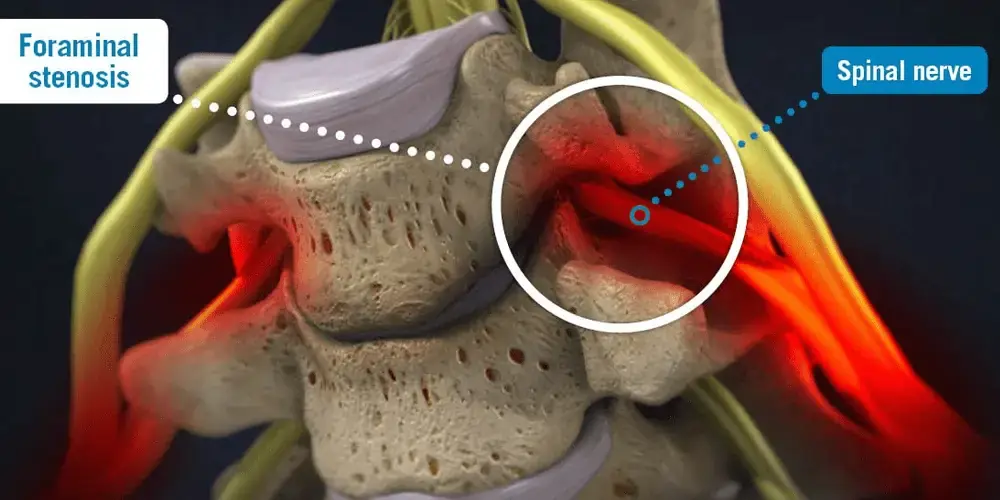
The narrowing of the intervertebral foramen, a little opening through which nerves leave our spinal canal and pass through our bodies, is known as neural foraminal stenosis. The term “neural,” which means “relating to a nerve” or “having to do with nerve cells,” is frequently added to the name of the condition.
Pain, numbness, pins and needles or tingling, weakness, and other symptoms of foraminal stenosis may be experienced as foraminal constriction starts to compress the nerves. You can experience symptoms in your hands, arms, and shoulders if the constriction affects the nerves in your neck.You will experience symptoms in your legs, foot, and buttocks if you have foraminal stenosis in your lower back.
Types of this Condition
Neural foramina are the orifices through which spinal nerves exit your spine and go to different areas of your body.The location of the opening in your spine determines its size. The type of foraminal stenosis also depends on where it is located.
From top to bottom, the many parts of your spine are as follows:
- Cervical vertebrae (neck). This region is the second most frequently affected by foraminal stenosis.
- Thoracic spine, which includes the middle and upper back.
- Back vertebrae (lumbar). This is the most typical location for foraminal stenosis.
- Lower back or lumbar spine. When foraminal stenosis occurs, this is the most typical location.
- The tailbone, or coccygeal spine, is pronounced “cah-kij-ee-u.”
What Are The Symptoms Of Foraminal Stenosis?
The symptoms of foraminal stenosis resemble those of radiculopathy or a pinched nerve.
One or more of the following symptoms, arranged from least to most severe, may be present:
- Pain
- Paresthesia is the feeling of tingling or “pins and needles.”
- numbness
- lack of control or weakening in the muscles
What are the causes of Foraminal Stenosis?
Your bones have degenerative changes as you age, which is a normal aspect of growing older. Spinal stenosis is most commonly caused by osteoarthritis. Your vertebral cushioning disc shrinks and dries out.Bone mass is lost. Bone spurs form. Stress and strain might cause your facet joints to swell. This is an attempt on the part of the body to disperse stress over more space. As a facet joint gets bigger, the spinal nerve has less room to go via the nerve root canal.
Numerous degenerative diseases like spondylosis or spondylolisthesis, trauma, vertebral fracture, and dislocation, skeletal disorders like rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis, or metabolic disorders like Paget’s disease or fluorosis—an excess of fluoride in the body—can also result in stenosis.
How Is An Illness Diagnosed?
See your family physician as soon as you feel any pain. In order to comprehend your symptoms, any past injuries or diseases, and ascertain whether any lifestyle choices are contributing to the pain, your pain doctor in Dallas will obtain a thorough medical history to better understand and effectively treat your condition. A physical examination is then conducted to identify the cause of the discomfort and check for any numbness or weakening in the muscles.
The following imaging tests could be requested by your doctor: an X-ray, an MRI, a myelogram, a CT scan, or an artery Doppler study. You might be referred to a neurosurgeon, orthopedist, or neurologist for therapy depending on the findings.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
(MRI) is a noninvasive procedure that provides a thorough image of your spine’s soft tissues by using radiofrequency radiation and a magnetic field. Nerves and discs are easily apparent, unlike with an X-ray. A dye (contrast agent) may or may not be introduced into your bloodstream during the procedure. In addition to nerve compression, MRI can identify spinal malignancies, abscesses, and bone overgrowth.
-
Myelogram
A myelogram is a type of specialist X-ray in which a spinal tap is used to introduce dye into the spinal canal. The dye-created pictures are subsequently captured by an X-ray fluoroscopy. Myelograms can reveal spinal cord malignancies, bone overgrowth, spinal abscesses, and ruptured discs pinching a nerve.The myelogram dye causes the X-ray to appear white, which gives the doctor a close-up picture of the spinal cord and canal. A CT scan is performed after this test.
-
Computed Tomography (CT)
A CT scan is a safe, non-invasive procedure that creates two-dimensional images of your spine using a computer and an X-ray beam.A dye (contrast agent) may or may not be introduced into your bloodstream during the procedure. It is particularly helpful for observing alterations in skeletal structures.
-
Doppler Ultrasound
Doppler ultrasonography is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure that assesses blood as it passes through a blood vessel using reflected sound waves.. To rule out peripheral artery disease as the source of painful leg symptoms, this test may be carried out.
Initial Treatments
When a diagnosis of foraminal stenosis is made, the most typical course of treatment is using NSAIDS (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines) to reduce tissue edema before physical therapy is advised.A series of exercises aimed at the troubled region of your spine can typically be performed at home to start therapy. Stretching, when combined with anti-inflammatory medicine and the use of heat or cold therapy as needed, typically reacts effectively enough to provide relief from mild pain associated with foraminal constriction. Your pain physicians in Dallas can advise you on whether heat therapy or cold therapy is preferable for your specific situation, ensuring a tailored approach to pain management. These therapies are merely a first line of defense and are only able to lessen symptoms; they cannot cure them.
Surgical Treatments
Surgical procedures for foraminal stenosis may include one of the following:
-
Cervical Foraminotomy
A minimally invasive treatment called a cervical foraminotomy is used to treat foraminal stenosis. It entails extracting a small fragment of tissue or bone from the cervical spine that is compressing the nerve.The symptoms of a pinched nerve are lessened when the cause of the compression is removed because the cleft between the vertebrae that the nerve must pass through is widened.Because cervical foraminotomy only necessitates a little than one-inch incision through the back of the neck, it is regarded as minimally invasive surgery. The lamina, a little section of the vertebra, is removed by inserting a tube through this incision.The crushed area is then accessed using extremely specialized medical equipment in order to remove the bone or tissue.
-
Laminotomy
A common symptom of spinal disorders is a shooting pain through the extremities, which is caused by the lamina compressing the nerves in certain circumstances.This pain is typically caused by spinal stenosis, or narrowing of the spinal canal, although foraminal stenosis can also be treated with this minimally invasive surgery. While this process is comparable to a cervical foraminotomy, it specifically removes the painful section of the lamina using tools.











