The Future of the EV Charging Market: Trends, Technologies, and Opportunities
Introduction
The electric vehicle (EV) revolution is accelerating, reshaping the global transportation landscape. As EV adoption surges, the demand for robust, efficient, and accessible charging infrastructure becomes paramount. This article explores the future of the EV charging market, examining emerging trends, technological innovations, and the evolving ecosystem that supports sustainable mobility.
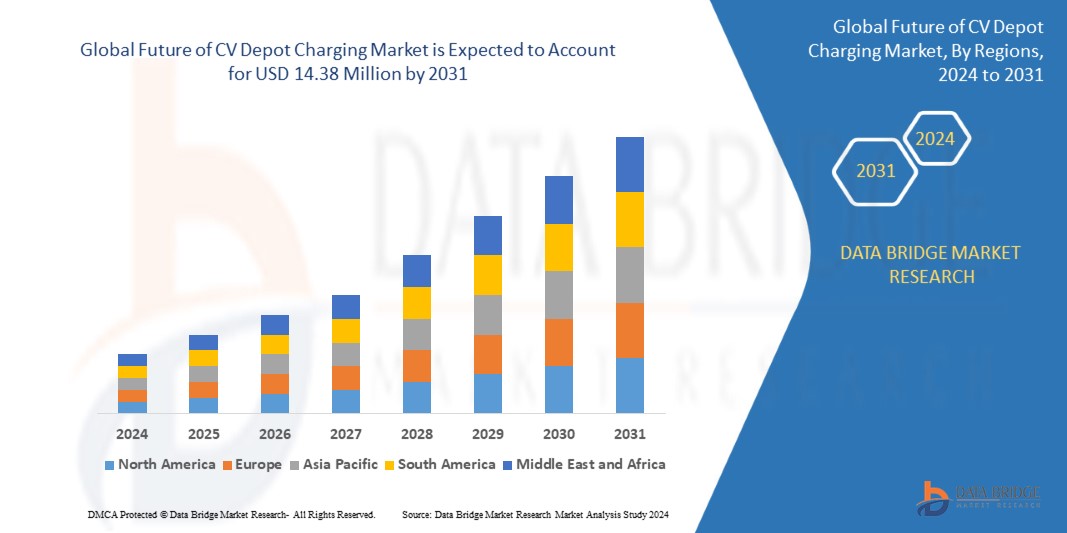
Source – https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-future-of-cv-depot-charging-market
1. Market Growth and Projections
The EV charging infrastructure market is experiencing rapid expansion, driven by increasing EV sales, supportive government policies, and technological advancements.
Global Outlook
-
Market Size: The global EV charging station market is projected to reach USD 480.57 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 26.89% from 2025 to 2034 .
-
Asia-Pacific Leadership: Asia-Pacific dominates the market, accounting for 49.78% share in 2024, with significant investments from countries like China, India, and Japan.
Indian Scenario
-
Infrastructure Expansion: India is witnessing a surge in charging infrastructure development. Tata.ev, for instance, has inaugurated its first 10 high-speed MegaChargers along major highways, aiming to expand to 400,000 charging points by 2027 .
-
Policy Support: The Delhi government’s revamped EV policy aims to create 20,000 jobs through the expansion of charging and battery swapping infrastructure, targeting 95% EV adoption among new vehicle registrations by 2027 .
2. Technological Innovations Shaping the Future
a. Ultra-Fast Charging
Advancements in charging technology are reducing charging times, enhancing user convenience.
-
High-Powered Chargers: Companies are developing ultra-fast chargers delivering 350+ kW, enabling 80% charges in just 15 minutes .
-
Zeekr’s V3 Superchargers: Zeekr introduced V3 Superchargers with 800 kW capability, allowing the Zeekr 001 model to recharge from 10% to 80% in under 12 minutes .
b. Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Integration
V2G technology enables bidirectional energy flow between EVs and the grid, enhancing grid stability and offering potential revenue streams for EV owners.
-
Grid Resilience: By 2025, V2G is expected to become mainstream, allowing EVs to return electricity to the grid during peak demand .
-
Virtual Power Plants: Initiatives like ChargeScape in the U.S. are establishing EV virtual power plants, optimizing electricity use during peak periods .
c. Renewable Energy Integration
Integrating renewable energy sources with charging infrastructure promotes sustainability and energy efficiency.
-
Solar-Powered Stations: Charging stations are increasingly incorporating solar panels and battery storage systems, reducing operational costs and environmental impact .
-
Second-Life Batteries: Repurposed EV batteries are being deployed in energy storage systems, enhancing energy resilience and reducing CO2 emissions .
d. Smart Charging and AI Integration
Artificial intelligence and smart technologies are optimizing charging operations and grid management.+1
-
AI-Powered Networks: Smart systems optimize energy distribution, predict maintenance needs, and enhance network efficiency .
-
Smart Load Balancing: These systems prevent grid overload and optimize power flow, reducing grid upgrade costs.
e. Wireless Charging
Wireless charging technologies offer cable-free solutions, enhancing user convenience.
-
Static and Dynamic Systems: Both static pads and dynamic road systems are under development, enabling vehicles to charge while parked or in motion .
3. Standardization and Interoperability
Standardization is crucial for seamless EV charging experiences across different platforms and regions.
-
ISO 15118: This standard enables Plug & Charge functionality, allowing EVs to automatically identify and authorize themselves to compatible charging stations .
-
Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP): OCPP facilitates communication between EV charging stations and central management systems, promoting interoperability .
4. Challenges and Considerations
a. Infrastructure Development
Despite progress, infrastructure development faces challenges, including high costs, land acquisition issues, and grid capacity constraints.
-
Grid Integration: Integrating charging stations with existing grids requires careful planning to prevent overloads and ensure reliability.
b. Cybersecurity Concerns
As charging infrastructure becomes more connected, cybersecurity becomes a critical concern.
-
Intrusion Detection Systems: Research is ongoing to develop machine-learning-based intrusion detection systems to safeguard EV charging ecosystems .
c. Standardization Hurdles
Lack of uniform standards across regions and manufacturers can hinder seamless EV adoption.
-
Connector Types: Variations in charging connector types (e.g., CCS, CHAdeMO) and grid capacities pose compatibility challenges .
5. Opportunities and Future Outlook
The EV charging market presents numerous opportunities for innovation, investment, and collaboration.
-
Job Creation: Expansion of charging infrastructure is expected to create significant employment opportunities, as seen in Delhi’s initiative to generate 20,000 jobs .
-
Private Sector Participation: Companies like Tata.ev are leading the way in infrastructure development, indicating a growing role for private players .
-
Global Collaboration: International cooperation on standards, technology sharing, and policy alignment can accelerate EV adoption and infrastructure development.
Conclusion
The future of the EV charging market is dynamic and promising, characterized by rapid technological advancements, supportive policies, and increasing consumer acceptance. Addressing challenges related to infrastructure, standardization, and cybersecurity will be crucial in realizing the full potential of electric mobility. With concerted efforts from governments, industry stakeholders, and consumers, the EV charging ecosystem is poised to become a cornerstone of sustainable transportation.





