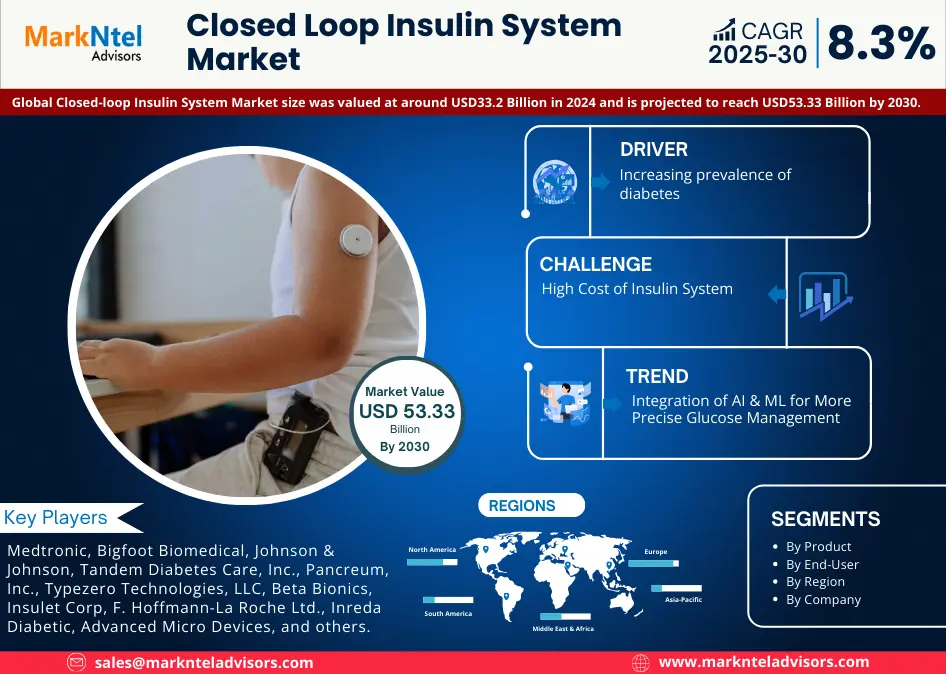
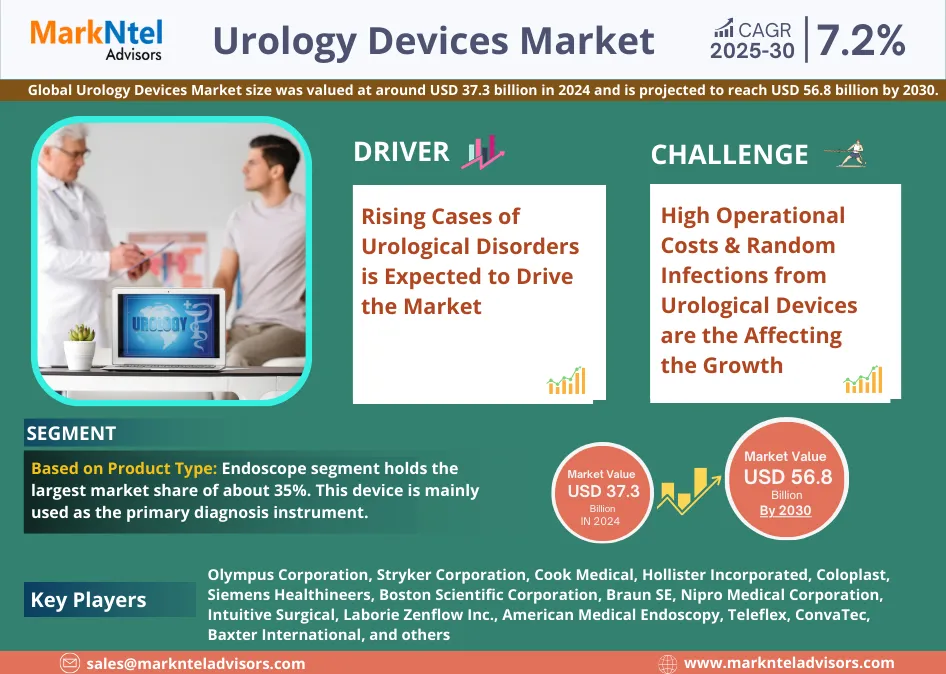
Accessibility in E-Learning: Making LMS Inclusive for All

In recent years, the landscape of education has undergone a transformative shift with the widespread adoption of e-learning platforms. As technology continues to redefine the way we learn, it is crucial to ensure that these digital environments are accessible to everyone, regardless of their abilities or disabilities. This blog post explores the importance of accessibility in e-learning and highlights the measures that can be taken to make Learning Management Systems (LMS) inclusive for all learners.
Understanding Accessibility in E-Learning:
Accessibility in learning management system refers to the design and development of digital educational content and platforms that can be easily navigated and understood by individuals with diverse abilities. This inclusivity extends to learners with disabilities such as visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments. An accessible e-learning environment ensures that all students, regardless of their physical or cognitive limitations, can participate fully in educational activities and access information without barriers.
Challenges Faced by Diverse Learners:
To comprehend the significance of accessibility in e-learning, it is essential to recognize the challenges faced by individuals with disabilities. Visual impairments may hinder the ability to read text or view images, while auditory impairments can affect one’s capacity to comprehend spoken instructions. Motor disabilities may make navigation through the interface difficult, and cognitive impairments can impact information processing and understanding.
Moreover, inaccessible e-learning environments can lead to exclusion and hinder the educational progress of students with disabilities. Recognizing these challenges is the first step towards creating a learning ecosystem that caters to the needs of all learners.
Importance of Accessibility in E-Learning:
- Equal Educational Opportunities: Accessibility ensures that all students have an equal opportunity to access educational resources, participate in discussions, and complete assignments. This promotes a more inclusive learning environment where diversity is celebrated.
- Legal and Ethical Obligations: Many countries have enacted laws and regulations that mandate accessible digital content in educational settings. Compliance with these laws not only fulfills legal obligations but also aligns with ethical principles of providing equal opportunities for education.
- Enhanced Learning Experience: Accessibility features not only benefit learners with disabilities but can enhance the overall learning experience for everyone. For instance, captions in videos not only assist those with hearing impairments but also benefit learners in noisy environments or those who prefer to read the content.
- Diverse Learning Styles: Students have diverse learning styles and preferences. By incorporating accessibility features, educators can accommodate these differences and create a more flexible and adaptable learning environment that caters to individual needs.
Making Learning Management Systems Inclusive:
- Responsive Design: Ensure that the LMS has a responsive design that adapts to various devices and screen sizes. This is particularly important for learners who use different devices or assistive technologies to access content.
- Alternative Text for Images: Include alternative text (alt text) for all images to describe their content. This benefits learners who use screen readers, as it provides a textual description of visual elements.
- Captioned and Transcribed Multimedia: Provide captions for videos and transcriptions for audio content. This benefits learners with hearing impairments and also aids those who may prefer reading the content.
- Keyboard Navigation: Ensure that all functionalities within the LMS software can be accessed and navigated using a keyboard. This is crucial for individuals with motor disabilities who may rely on keyboard input.
- Readable Font and Color Contrast: Use readable fonts and maintain sufficient color contrast to enhance readability. This benefits learners with visual impairments and ensures a comfortable reading experience for all.
- User-Friendly Interface: Design an intuitive and user-friendly interface that minimizes complexity. This benefits learners with cognitive impairments and promotes a smoother learning experience for everyone.
- Flexible Assessment Options: Provide flexible assessment options that accommodate diverse learning styles and abilities. For example, allow for extended time on exams for students who require it.
- Training for Educators: Educators play a crucial role in creating an inclusive learning environment. Providing training on accessibility guidelines and best practices ensures that they can design and deliver content that is accessible to all learners.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, making Learning Management Systems inclusive for all learners is not just a matter of compliance with legal standards; it is a commitment to providing equal educational opportunities to everyone. The benefits of accessibility extend beyond the realm of accommodating disabilities; they contribute to a more robust and adaptable learning environment that caters to the diverse needs and preferences of all learners. By prioritizing accessibility in e-learning, we pave the way for a future where education truly a universal right, accessible to every individual, regardless of their abilities or disabilities.